Real-world financial reporting examples
It can be easy to understand why financial reporting is important in the big-picture sense, but it might be tricky to understand the importance of this topic from the day-to-day lens. Below are some real-world examples of when financial reporting can be helpful to you and your small business.
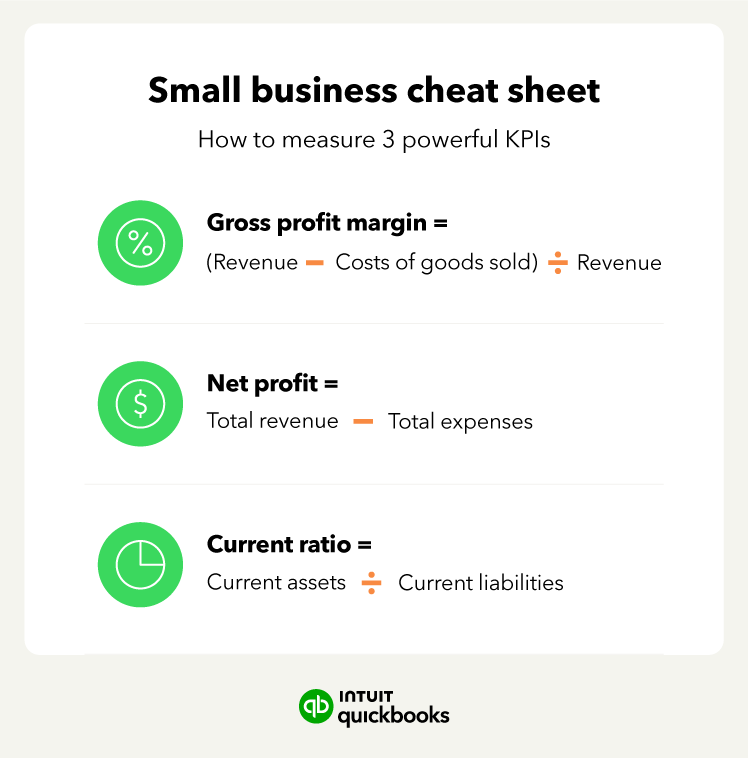
Profitability
Financial reports tell you at a glance how much money your business is making after your expenses are paid, or your profitability ratio. This is incredibly important information to know since profitability is what keeps your business thriving.
Stocks
Although not so obvious, financial reporting can have a major impact on a company’s stock price. Investors tend to look at financial statements when making investment decisions—if this information is better or worse than expected, it could swing the stock price in either direction. Oftentimes, investors use financial ratios based on the financial reports to make assumptions about the financial health of a company.
Capital
Whether you have a large financial cushion or have your money spread across several investments, it’s important to know exactly what kind of working capital you have at any particular time. For example, it’s important to know if you have the capital to make necessary upgrades to your equipment when needed.
Payroll
As a small business owner, an essential part of running a business is to make sure that your employees are paid. After all, no employee wants to work for free, so being able to make payroll on time is an important aspect of running a business smoothly. Financial reporting will help give you an idea of your cash flow to ensure that you won’t be putting yourself or your employees at risk for nonpayment.
Financial reporting: The backbone of your business success
While it may sound daunting, financial reporting is perhaps the most crucial thing a company can do. After all, this gives you the capability to make strategic and forward-thinking decisions for you and your business while maintaining compliance with the government. With proper financial forecasting, you’ll be able to take your business to the next level.
QuickBooks Online users can choose QuickBooks Live Assisted Bookkeeping to get year-round access to verified experts who are focused on their success. From the start, business owners can get personalized answers to questions, including topics like financial reporting.
*QuickBooks Live Bookkeeping requires QuickBooks Online subscription. Additional terms, conditions, limitations, and fees apply.